|
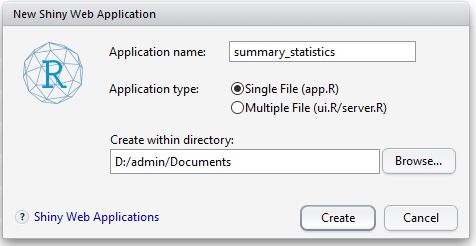
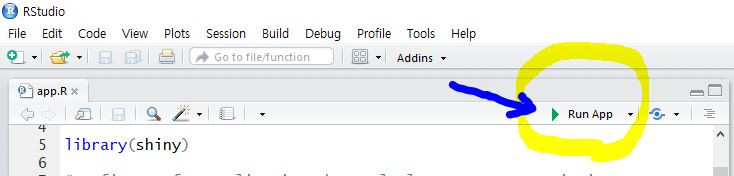
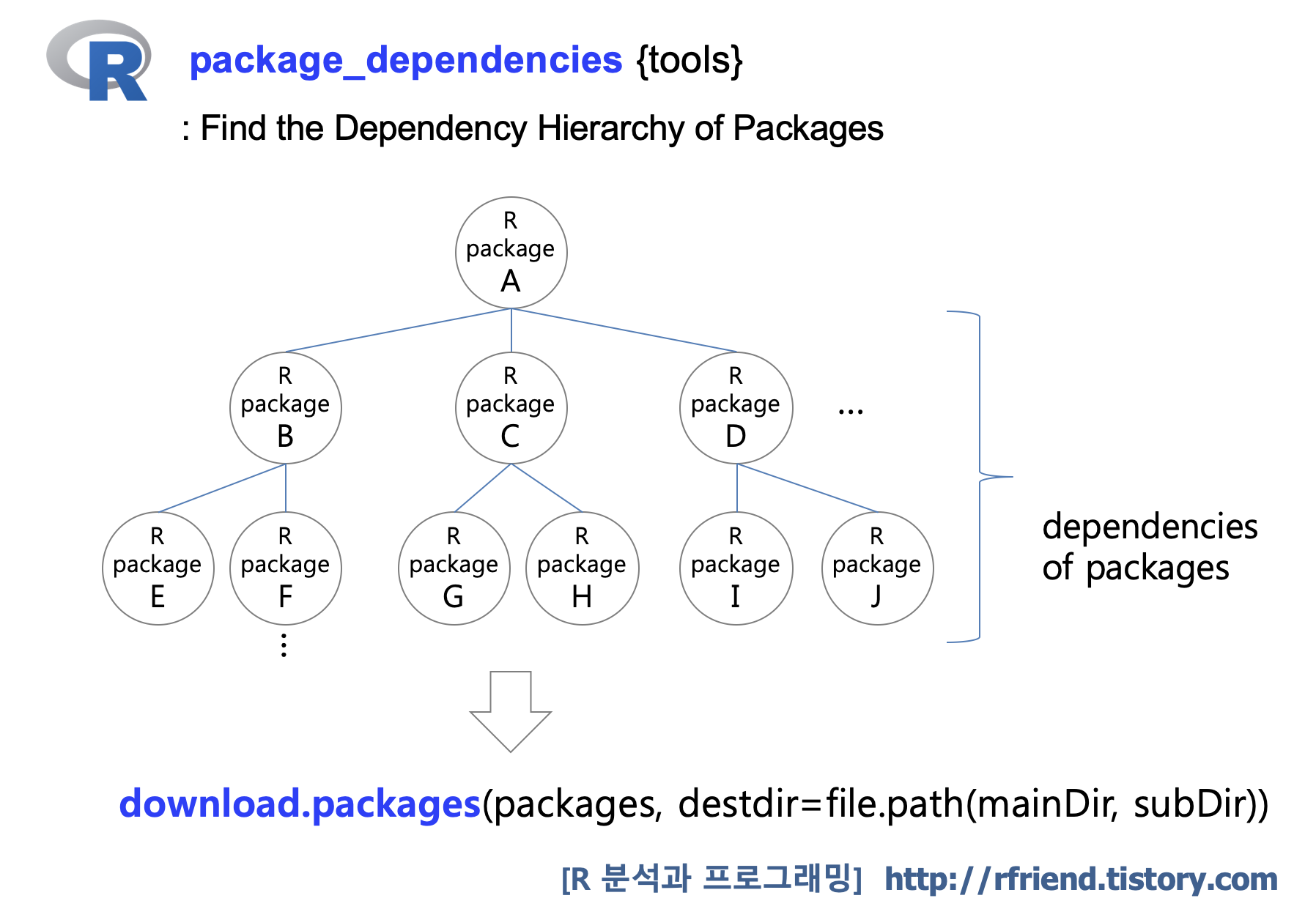
> packages <- getPackages(c("dplyr", "ggplot2"))
> download.packages(packages, destdir=file.path(mainDir, subDir))
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/dplyr_0.8.0.1.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 1075146 bytes (1.0 MB)
==================================================
downloaded 1.0 MB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/ggplot2_3.1.1.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 2862022 bytes (2.7 MB)
==================================================
downloaded 2.7 MB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/assertthat_0.2.1.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 12742 bytes (12 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 12 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/glue_1.3.1.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 122950 bytes (120 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 120 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/magrittr_1.5.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 200504 bytes (195 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 195 KB
Warning in download.packages(packages, destdir = file.path(mainDir, subDir)) :
no package 'methods' at the repositories
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/pkgconfig_2.0.2.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 6024 bytes
==================================================
downloaded 6024 bytes
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/R6_2.4.0.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 31545 bytes (30 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 30 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/Rcpp_1.0.1.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 3661123 bytes (3.5 MB)
==================================================
downloaded 3.5 MB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/rlang_0.3.4.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 858992 bytes (838 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 838 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/tibble_2.1.1.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 311836 bytes (304 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 304 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/tidyselect_0.2.5.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 21883 bytes (21 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 21 KB
Warning in download.packages(packages, destdir = file.path(mainDir, subDir)) :
no package 'utils' at the repositories
Warning in download.packages(packages, destdir = file.path(mainDir, subDir)) :
no package 'tools' at the repositories
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/cli_1.1.0.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 40232 bytes (39 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 39 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/crayon_1.3.4.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 658694 bytes (643 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 643 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/fansi_0.4.0.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 266123 bytes (259 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 259 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/pillar_1.3.1.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 103972 bytes (101 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 101 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/purrr_0.3.2.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 373701 bytes (364 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 364 KB
Warning in download.packages(packages, destdir = file.path(mainDir, subDir)) :
no package 'grDevices' at the repositories
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/utf8_1.1.4.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 218882 bytes (213 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 213 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/digest_0.6.18.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 128553 bytes (125 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 125 KB
Warning in download.packages(packages, destdir = file.path(mainDir, subDir)) :
no package 'grid' at the repositories
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/gtable_0.3.0.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 368081 bytes (359 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 359 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/lazyeval_0.2.2.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 83482 bytes (81 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 81 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/MASS_7.3-51.4.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 487233 bytes (475 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 475 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/mgcv_1.8-28.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 915991 bytes (894 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 894 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/plyr_1.8.4.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 392451 bytes (383 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 383 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/reshape2_1.4.3.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 36405 bytes (35 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 35 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/scales_1.0.0.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 299262 bytes (292 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 292 KB
Warning in download.packages(packages, destdir = file.path(mainDir, subDir)) :
no package 'stats' at the repositories
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/viridisLite_0.3.0.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 44019 bytes (42 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 42 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/withr_2.1.2.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 53578 bytes (52 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 52 KB
Warning in download.packages(packages, destdir = file.path(mainDir, subDir)) :
no package 'graphics' at the repositories
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/nlme_3.1-139.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 793473 bytes (774 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 774 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/Matrix_1.2-17.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 1860456 bytes (1.8 MB)
==================================================
downloaded 1.8 MB
Warning in download.packages(packages, destdir = file.path(mainDir, subDir)) :
no package 'splines' at the repositories
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/stringr_1.4.0.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 135777 bytes (132 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 132 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/labeling_0.3.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 10722 bytes (10 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 10 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/munsell_0.5.0.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 182653 bytes (178 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 178 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/RColorBrewer_1.1-2.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 11532 bytes (11 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 11 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/lattice_0.20-38.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 359031 bytes (350 KB)
==================================================
downloaded 350 KB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/colorspace_1.4-1.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 2152594 bytes (2.1 MB)
==================================================
downloaded 2.1 MB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/src/contrib/stringi_1.4.3.tar.gz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 7290890 bytes (7.0 MB)
==================================================
downloaded 7.0 MB
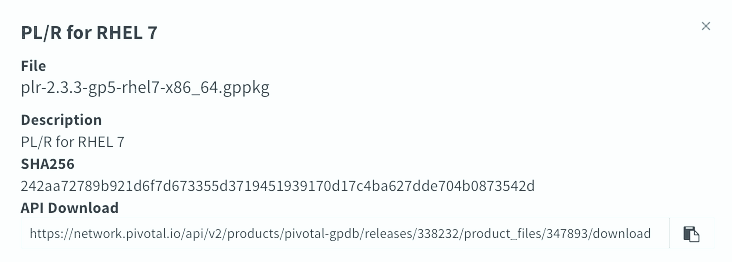
[,1] [,2]
[1,] "dplyr" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/dplyr_0.8.0.1.tar.gz"
[2,] "ggplot2" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/ggplot2_3.1.1.tar.gz"
[3,] "assertthat" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/assertthat_0.2.1.tar.gz"
[4,] "glue" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/glue_1.3.1.tar.gz"
[5,] "magrittr" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/magrittr_1.5.tar.gz"
[6,] "pkgconfig" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/pkgconfig_2.0.2.tar.gz"
[7,] "R6" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/R6_2.4.0.tar.gz"
[8,] "Rcpp" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/Rcpp_1.0.1.tar.gz"
[9,] "rlang" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/rlang_0.3.4.tar.gz"
[10,] "tibble" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/tibble_2.1.1.tar.gz"
[11,] "tidyselect" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/tidyselect_0.2.5.tar.gz"
[12,] "cli" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/cli_1.1.0.tar.gz"
[13,] "crayon" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/crayon_1.3.4.tar.gz"
[14,] "fansi" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/fansi_0.4.0.tar.gz"
[15,] "pillar" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/pillar_1.3.1.tar.gz"
[16,] "purrr" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/purrr_0.3.2.tar.gz"
[17,] "utf8" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/utf8_1.1.4.tar.gz"
[18,] "digest" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/digest_0.6.18.tar.gz"
[19,] "gtable" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/gtable_0.3.0.tar.gz"
[20,] "lazyeval" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/lazyeval_0.2.2.tar.gz"
[21,] "MASS" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/MASS_7.3-51.4.tar.gz"
[22,] "mgcv" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/mgcv_1.8-28.tar.gz"
[23,] "plyr" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/plyr_1.8.4.tar.gz"
[24,] "reshape2" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/reshape2_1.4.3.tar.gz"
[25,] "scales" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/scales_1.0.0.tar.gz"
[26,] "viridisLite" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/viridisLite_0.3.0.tar.gz"
[27,] "withr" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/withr_2.1.2.tar.gz"
[28,] "nlme" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/nlme_3.1-139.tar.gz"
[29,] "Matrix" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/Matrix_1.2-17.tar.gz"
[30,] "stringr" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/stringr_1.4.0.tar.gz"
[31,] "labeling" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/labeling_0.3.tar.gz"
[32,] "munsell" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/munsell_0.5.0.tar.gz"
[33,] "RColorBrewer" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/RColorBrewer_1.1-2.tar.gz"
[34,] "lattice" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/lattice_0.20-38.tar.gz"
[35,] "colorspace" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/colorspace_1.4-1.tar.gz"
[36,] "stringi" "/Users/ihongdon/Downloads/r-pkg/stringi_1.4.3.tar.gz"
|
![]() '를 꾹 눌러주세요. :-)
'를 꾹 눌러주세요. :-)