[LangChain] 시맨틱 유사도를 통해 질문과 유사한 템플릿으로 라우팅하기
Deep Learning (TF, Keras, PyTorch)/Natural Language Processing 2023. 12. 31. 18:22LangChain과 LLM 모델을 사용하여 애플리케이션을 만들 때 필요에 따라서 여러개의 템플릿(templates)을 미리 작성해 놓고, 사용자의 질문과 가장 유사한 (most similar, most relavant) 템플릿을 선택해서 LLM 모델로 질문과 템플릿을 인풋으로 보낼 수 있다면 보다 맞춤형의 답변을 생성할 수 있을 것입니다.
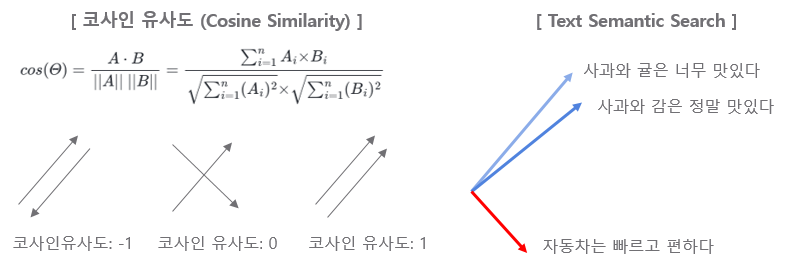
시맨틱 검색은 임베딩과 코사인 유사도를 사용하는 것은 자연어 처리 및 정보 검색에서 검색 결과의 관련성과 정확성을 향상시키기 위해 쿼리의 의미에 기반하여 사용되는 방법입니다.
1. 시맨틱 검색 (Semantic Search): 전통적인 검색 엔진은 종종 정확한 키워드 일치에 의존합니다. 반면에 시맨틱 검색은 검색 쿼리의 의도와 맥락적 의미를 이해하려고 합니다. 동의어, 관련 용어 및 전체 맥락과 같은 언어의 뉘앙스를 해석하여 더욱 관련성 높은 결과를 제공하려고 합니다.
2. 임베딩 (Embeddings): 시맨틱 이해를 달성하기 위해 시스템은 임베딩을 사용합니다. 임베딩은 단어, 구, 문장 또는 전체 문서를 고차원 공간에서 수치적으로 표현한 것입니다. 이러한 표현은 대규모 데이터셋에서 학습되며 단어 간의 의미 관계를 포착합니다. 예를 들어, 잘 훈련된 임베딩 공간에서는 유사한 의미를 가진 단어들이 서로 가까이 위치합니다.
3. 코사인 유사도 (Cosine Similarity): 텍스트(검색 쿼리와 검색 가능한 문서 모두)를 임베딩으로 변환한 후, 시스템은 얼마나 유사한지 측정할 방법이 필요합니다. 이를 위해 흔히 사용되는 척도는 코사인 유사도입니다. 코사인 유사도는 두 벡터(이 경우, 쿼리와 문서의 임베딩) 사이의 각도의 코사인을 측정합니다. 코사인 유사도가 1에 가까우면 매우 작은 각도를 나타내고, 따라서 높은 유사도를 의미합니다. 반대로, 코사인 유사도가 0에 가까우면 큰 각도와 낮은 유사도를 나타냅니다.
4. 검색에서의 적용 (Application in Search): 사용자가 쿼리를 제출하면, 시스템은 이를 임베딩으로 변환한 다음 이 임베딩과 데이터베이스의 다양한 문서들의 임베딩 간의 코사인 유사도를 계산합니다. 코사인 유사도 점수가 더 높은 문서는 쿼리와 더 관련이 있다고 간주되어 검색 결과에서 더 높은 순위를 차지합니다.
이러한 접근 방식은 시스템이 사용자 쿼리의 의미적 내용을 더 잘 포착하고 응답할 수 있게 하여, 단순히 특정 단어를 일치시키는 것보다 더 미묘하고 효과적인 검색 경험을 가능하게 합니다.
[ 코사인 유사도와 시맨틱 검색 ]
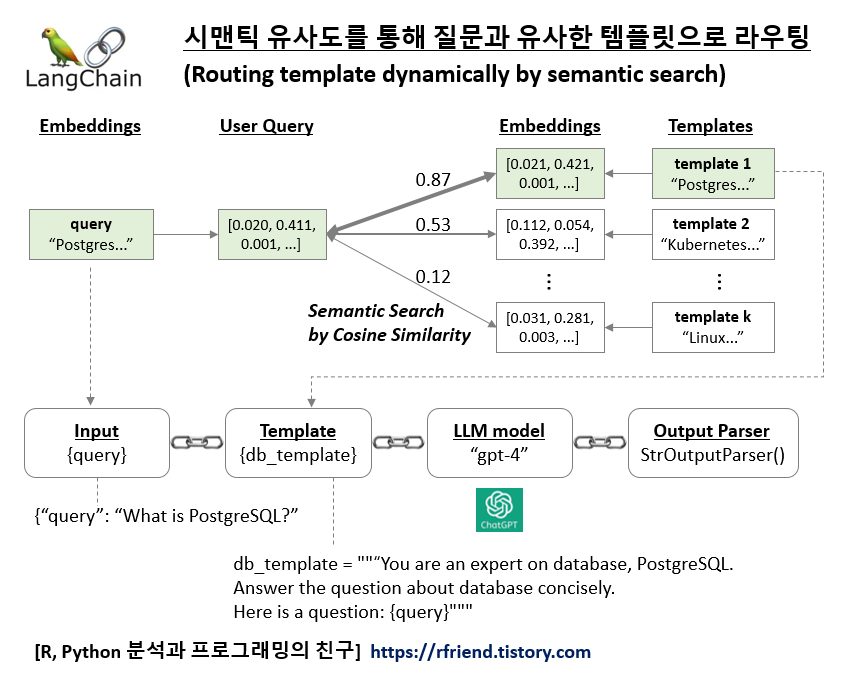
LangChain과 ChatGPT LLM 모델을 사용해서 여러개의 템플릿을 미리 만들어놓고 질문에 가장 유사한 템플릿을 선택해서 대답을 생성하는 간단한 챗봇을 만들어보겠습니다.
먼저, 터미널에서 langchain, openai, tiktoken 모듈을 pip install을 사용해서 설치합니다.
! pip install -q langchain openai tiktoken
OpenAI의 ChatGPT를 LLM 모델로 사용할 것이므로 OpenAI API Key를 등록해줍니다.
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-xxxx..."
필요한 모듈을 import 하고, Database PostgreSQL 과 관련된 template 1, 그리고 Cloud Kubernetes Docker 관련된 template 2 를 각각 정의해 줍니다.
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.utils.math import cosine_similarity
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableLambda, RunnablePassthrough
# Template 1: Database PostgreSQL
database_template = """You are an expert on database, especially open source PostgreSQL.
You are good at answering questions about database in a concise manner.
Here is a question:
{query}"""
# Template 2: Colud, Kubernetes, Docker
cloud_template = """You are an expert on cloud platform.
You are good at answering questions especially on kubernetes and docker.
The user is from Korean. Answer the question in Korean.
Here is a question:
{query}
"""
Text Embedding 모델로는 OpenAI의 1,536 차원을 가진 "text-embedding-ada-002" 를 사용하겠습니다.
- 여러개의 텍스트에 대해서는 embeddings.embed_documents(),
- 하나의 query에 대해서는 embeddings.embed_query()
메소드를 사용해서 텍스트를 임베딩으로 변환합니다.
# OpenAI Embeddings: https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/embeddings
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(model="text-embedding-ada-002")
prompt_templates = [database_template, cloud_template]
prompt_embeddings = embeddings.embed_documents(prompt_templates)
query_embedding = embeddings.embed_query("What is PostgreSQL database?")
len(query_embedding)
# 1536
len(prompt_embeddings[0])
# 1536
query_embedding[:10]
# [0.011614119106739642,
# -0.011661718070044624,
# -0.011185729368317337,
# -0.02718574244037603,
# -0.043219754372800054,
# 0.02449300773999799,
# -0.006510842295925382,
# 0.00851339435668751,
# -0.021011491283506004,
# -0.018604350362957857]
임베딩과 시맨틱 검색 (semantic search) 이 잘 작동하는지를 확인하기 위해 아래에 PostgreSQL Database, K8s and Docker 관련된 질문을 각각 해봤습니다. 코사인(Cosine Similarity)는 -1~1 사이의 값을 가지면 1에 가까울 수록 서로 유사하다고 판단할 수 있는데요, 첫번째 PostgreSQL 관련 질문에는 database_template 이 유사하다고 나왔고, 두번째 K8s and Docker 관련 짊누에서는 cloud_template 이 더 유사한 것으로 나왔으니 의도한 대로 잘 작동하네요.
# Question 1: PostgreSQL database
query_embedding = embeddings.embed_query("What is PostgreSQL database?")
similarity = cosine_similarity([query_embedding], prompt_embeddings)[0]
print(similarity)
# [0.8684732 0.74399373]
# Question 2: K8s, Docker
query_embedding = embeddings.embed_query("What is Kubernetes and Docker?")
similarity = cosine_similarity([query_embedding], prompt_embeddings)[0]
print(similarity)
# array([0.75842006, 0.83432307])
템플릿들(templates)과 사용자 질문(user query) 텍스트를 임베딩으로 변환
--> cosine_similarity() 메소드로 템플릿과 질문 간 임베딩 간 코사인 유사도 계산
--> 질문과 가장 유사한 템플릿 선택하여 반환
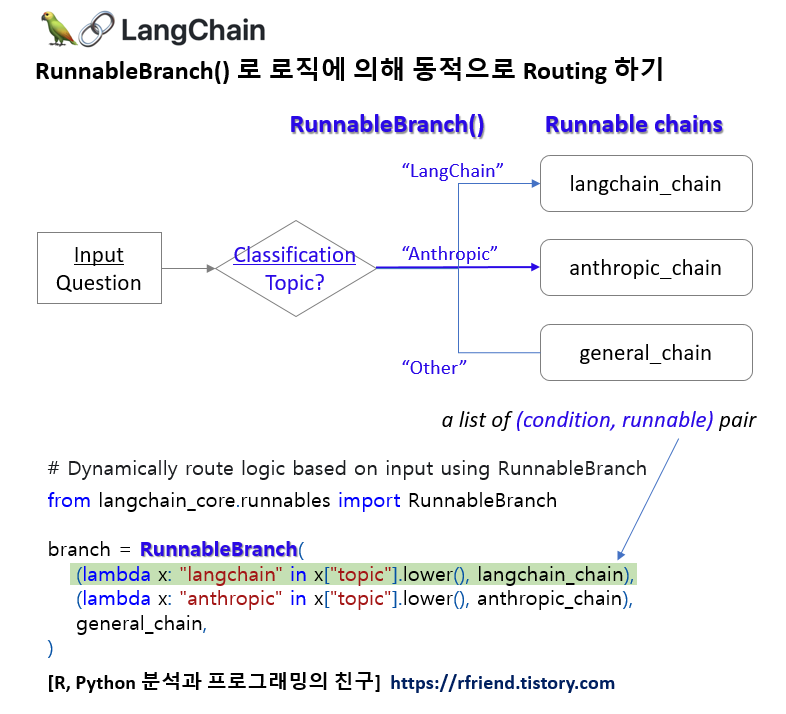
하는 과정을 prompt_router(input) 사용자 정의 함수로 정의해줍니다.
그리고 langchain_core.runnables.RunnableLambda(prompt_router) 를 사용해서
그리고 '|'를 사용해서
템플릿들(templates)과 사용자 질문(user query) 텍스트를 임베딩으로 변환
--> 템플릿과 질문 간 임베딩 간 코사인 유사도 계산 (calculate cosine similarity)
--> 질문과 가장 유사한 템플릿 선택하여 반환
--> 질문과 가장 유사한 템플릿을 사용하여 ChatGPT 모델로 답변 생성
--> ChatGPT 답변을 String으로 파싱하여 반환
하는 일련의 과정을 chaining 해주었습니다.
# Define a UDF for routing prompts dynamically
def prompt_router(input):
query_embedding = embeddings.embed_query(input["query"])
similarity = cosine_similarity([query_embedding], prompt_embeddings)[0]
most_similar = prompt_templates[similarity.argmax()]
print("Using Database" if most_similar == database_template else "Using Cloud")
return PromptTemplate.from_template(most_similar)
# Chaining
chain = (
{"query": RunnablePassthrough()}
| RunnableLambda(prompt_router)
| ChatOpenAI()
| StrOutputParser()
)
앞에서 정의한 chain을 invoke() 메소드를 사용해서 실행시켜줍니다.
chain.invoke("What is PostgreSQL database?")
# Using Database
# 'PostgreSQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS)
# that offers advanced features and strong data integrity. It is widely known
# for its robustness, scalability, and SQL compliance.
# PostgreSQL supports various data types, including structured, semi-structured,
# and unstructured data, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
# It offers features like ACID compliance, MVCC, JSON support, full-text search,
# and extensive extensibility through procedural languages and extensions.
# PostgreSQL is highly customizable and can be used for small to large-scale applications,
# making it a popular choice among developers and enterprises.'
의도한 대로, 그리고 템플릿에 지시문을 작성한 대로 잘 작동하네요.
(cloud_template 에는 사용자가 한국인이므로 한글로 답변을 생성하라고 지시문을 추가했었습니다.)
chain.invoke("What is Kubernetes and Docker?")
# Using Cloud
# 'Kubernetes와 Docker는 모두 컨테이너화된 애플리케이션을 관리하기 위한 클라우드 플랫폼 도구입니다.
# Docker는 컨테이너 기반 가상화 기술을 제공하는 플랫폼입니다.
# 컨테이너는 애플리케이션을 격리된 환경에서 실행하고, 이식성과 확장성을 높여줍니다.
# Docker는 애플리케이션의 종속성을 패키징하고 배포할 수 있도록 도와주며,
# 애플리케이션을 컨테이너 이미지로 만들어 관리합니다.
# Kubernetes는 컨테이너 오케스트레이션 플랫폼으로, 도커 컨테이너의 배포, 확장, 관리를
# 자동화합니다. Kubernetes는 여러 호스트에 걸쳐 컨테이너를 스케줄링하고, 서비스 디스커버리,
# 로드 밸런싱, 자가 치유 등의 기능을 제공하여 애플리케이션 운영을 단순화합니다.
# 또한 Kubernetes는 컨테이너의 상태를 모니터링하고 필요한 조치를 취할 수 있어
# 안정적인 운영을 지원합니다.\n\n요약하자면, Docker는 컨테이너 기반 가상화 기술을 제공하고,
# Kubernetes는 컨테이너 오케스트레이션 플랫폼으로
# 컨테이너화된 애플리케이션의 배포와 관리를 용이하게 해주는 도구입니다.'
[ Reference ]
* LangChain - Routing by semantic similarity:
https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/cookbook/embedding_router
* OpenAI Embeddings: https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/embeddings/what-are-embeddings
이번 포스팅이 많은 도움이 되었기를 바랍니다.
행복한 데이터 과학자 되세요. :-)