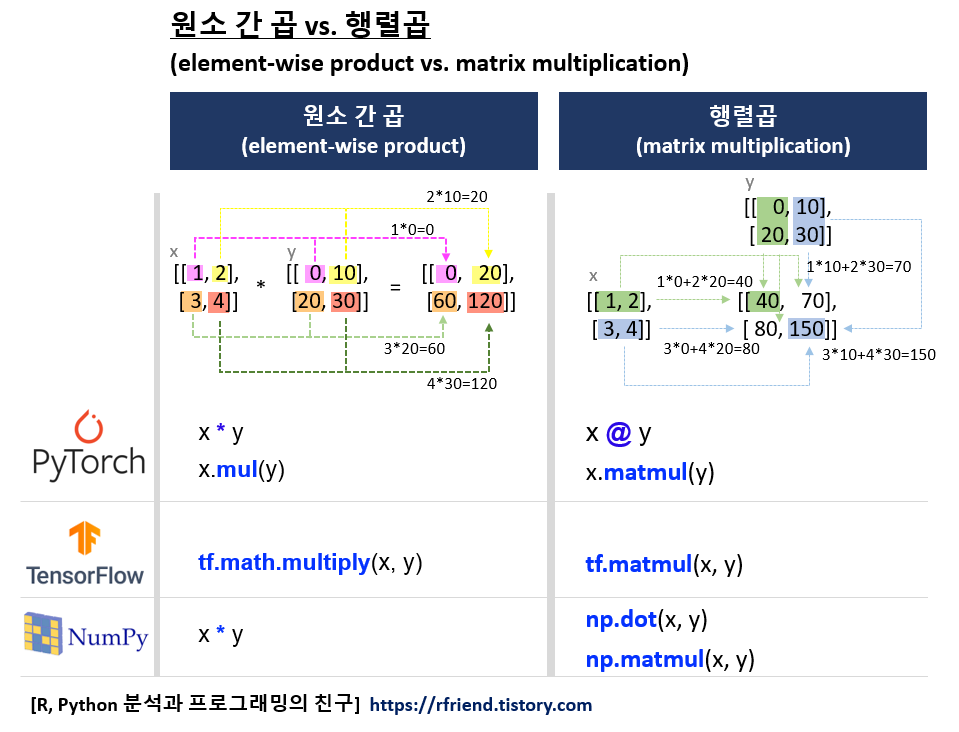
[PyTorch] 원소 간 곱 vs. 행렬곱 (element-wise product vs. matrix multiplication)
Deep Learning (TF, Keras, PyTorch)/PyTorch basics 2023. 12. 16. 10:37이번 포스팅에서는 PyTorch 를 사용해서 두 개 Tensor 에 대해
(1) 원소 간 곱 (Element-wise Product)
(2) 행렬 곱 (Matrix Multiplication)
하는 방법을 비교해서 소개하겠습니다.
먼저, 간단한 예제로 torch.size([2, 2]) 형태를 가지는 x, y 두 개의 Tensor 객체를 만들어보겠습니다.
그리고 shape, dtype (data type), 저장되어 있는 device 를 확인해보겠습니다.
import torch
x = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
y = torch.tensor([[0, 10], [20, 30]])
print(f"Tensor x: \n {x}")
print(f"Shape of tensor x: {x.shape}")
print(f"Datatype of tensor x: {x.dtype}")
print(f"Device tensor x is stored: {x.device}")
print("----" * 15)
print(f"Tensor y: \n {y}")
print(f"Shape of tensor y: {y.shape}")
print(f"Datatype of tensor y: {y.dtype}")
print(f"Device tensor y is stored: {y.device}")
# Tensor x:
# tensor([[1, 2],
# [3, 4]])
# Shape of tensor x: torch.Size([2, 2])
# Datatype of tensor x: torch.int64
# Device tensor x is stored: cpu
# ------------------------------------------------------------
# Tensor y:
# tensor([[ 0, 10],
# [20, 30]])
# Shape of tensor y: torch.Size([2, 2])
# Datatype of tensor y: torch.int64
# Device tensor y is stored: cpu
(1) 원소 간 곱 (Element-wise Product)
원소 간 곱은 Tensor 내 같은 위치에 있는 원소 간 산술 곱을 해줍니다.
# (1) Element-wise product
# *, mul() is for element-wise multiplication,
# where each element in the resulting tensor is the product
# of the corresponding elements in the input tensors.
x * y
# tensor([[ 0, 20],
# [ 60, 120]])
x.mul(y)
# tensor([[ 0, 20],
# [ 60, 120]])
(2) 행렬 곱 (Matrix Multiplication)
행렬 곱은 선형대수 (Linear Algebra) 의 규칙을 따라서 행렬 곱을 해줍니다. (위의 예제 풀이 그림 참조)
# (2) Matrix Multiplication
# @, matmul() is for matrix or batched matrix multiplication,
# following the rules of linear algebra.
x @ y
# tensor([[ 40, 70],
# [ 80, 150]])
x.matmul(y)
# tensor([[ 40, 70],
# [ 80, 150]])
행렬 곱을 할 때 두 Tensor 간 shape 에 대해서 조심해야 할 것이 있습니다.
만약 첫번 째 행렬의 열의 개수와 두번 째 행렬의 행의 개수가 서로 일치하지 않은면 RuntimeError 가 발생합니다.
z = torch.tensor([[5, 6], [7, 8], [9, 10]])
print(f"Shape of tensor z: {z.shape}")
# Shape of tensor z: torch.Size([3, 2])
# RuntimeError: mat1 and mat2 shapes cannot be multiplied (2x2 and 3x2)
# due to a matrix multiplication between two matrices with shapes that are incompatible
x.matmul(z) # RuntimeError
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# RuntimeError Traceback (most recent call last)
# <ipython-input-42-0a2708938308> in <cell line: 2>()
# 1 # RuntimeError: mat1 and mat2 shapes cannot be multiplied (2x2 and 3x2)
# ----> 2 x.matmul(z)
# RuntimeError: mat1 and mat2 shapes cannot be multiplied (2x2 and 3x2)
따라서, 두 Tensor 간 행렬 곱을 할 때는 첫번 째 행렬의 열과 두번 째 행렬의 행의 개수를 일치시켜야 합니다.
행렬 A 가 (m x n), 행렬 B 가 (n x p) 의 형태를 가지고 있다면 행렬 A와 행렬 B 간의 행렬 곱 (matrix multiplication of A and B) 은 (m x p) 형태의 행렬 곱 결과를 반환합니다.
# In matrix multiplication,
# the number of columns in the first matrix
# must equal the number of rows in the second matrix.
# In other words, if the shape of the first matrix is (m x n),
# the shape of the second matrix must be (n x p) in order to multiply them,
# resulting in a new matrix of shape (m x p).
A = torch.randn(2, 3)
B = torch.randn(3, 2)
C = torch.matmul(A, B) # This will result in a matrix of shape 2x2
print(f"Shape of tensor C: {C.shape}")
# Shape of tensor C: torch.Size([2, 2])
이번 포스팅이 많은 도움이 되었기를 바랍니다.
행복한 데이터 과학자 되세요. :-)

'Deep Learning (TF, Keras, PyTorch) > PyTorch basics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [PyTorch] 모델을 저장하고, 다시 로딩하기 (Saving and Loading the model) (0) | 2023.12.17 |
|---|---|
| [PyTorch] 데이터셋 불러오고(Dataset), 변환하고(Transforms), iterable 하게 로딩하기(DataLoader) (0) | 2023.12.16 |
| 기울기 소실 문제(Vanishing Gradient Problem)란 무엇이고, 어떻게 완화할 수 있나? (0) | 2023.12.13 |
| 딥러닝에서 오차역전파법 (Backpropagation, Backward Propagation of Errors) 이란? (0) | 2023.12.12 |
| [PyTorch] torchvision.datasets 모듈에 내장되어 있는 데이터 가져와서 시각화하기 (0) | 2023.02.26 |