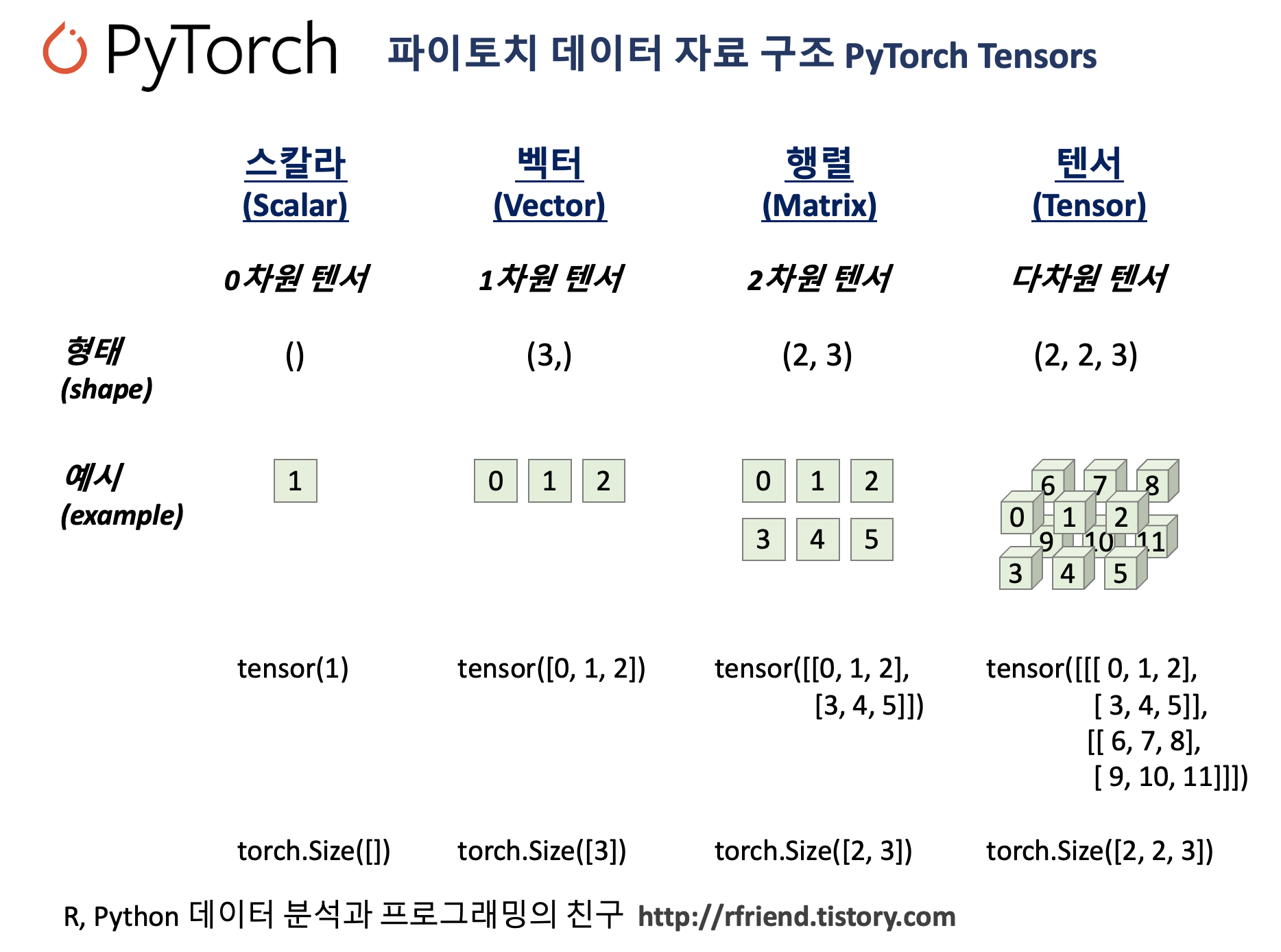
[PyTorch] 난수를 생성해서 텐서 만들기 (generating a tensor with random numbers)
Deep Learning (TF, Keras, PyTorch)/PyTorch basics 2023. 2. 12. 23:38이번 포스팅에서는 PyTorch 모듈을 사용해서 난수를 생성하여 텐서 객체를 만드는 여러가지 방법을 소개하겠습니다. (numpy 유사하네요)
1. 난수를 생성해서 PyTorch tensor를 만들기
(1-1) torch.rand(size) : 0과 1 사이의 실수[0, 1) 로 난수를 생성해서 텐서 만들기
(1-2) torch.randn(size) : 표준정규분포 X~N(0, 1)로 부터 난수를 생성해서 텐서 만들기
(1-3) torch.randint(low, high, size) : low~high 사이의 정수로 난수를 생성해서 텐서 만들기
(1-4) torch.randperm(the upper bound, n) : 0~n 사이의 정수를 무작위로 섞어서 텐서 만들기
2. 인풋과 동일한 형태(same shape as input tensor)로 난수를 생성해서 PyTorch tensor 만들기
(2-1) torch.rand_like(input) : 인풋과 동일한 형태(shape)로 0~1 사이의 실수로 난수를 생성해서 텐서 만들기
(2-2) torch.randn_like(input) : 인풋과 동일한 형태로 표준정규분포 X~N(0,1)에서 난수를 생성해서 텐서 만들기
(2-3) torch.randint_like(input, low, high) : 인풋과 동일한 형태로 low~high 사이의 정수로 난수를 생성해서 텐서 만들기

1. 난수를 생성해서 PyTorch tensor를 만들기
(1-1) torch.rand(size) : 0과 1 사이의 실수[0, 1) 로 난수를 생성해서 텐서 만들기
이때 0은 포함되고 1은 포함되지 않습니다. 난수를 생성하는 것이기 때문에 실행할 때마다 매번 텐서 안의 원소 값이 달라집니다.
import torch
## generating a tensor object with random numbers b/w 0 and 1
torch.rand(2, 4)
# tensor([[0.6653, 0.6714, 0.4876, 0.2055],
# [0.9733, 0.5680, 0.9754, 0.1981]])
만약, 난수 생성 값을 매번 동일하게 나오게 하고 싶다면 torch.manual_seed() 메소드로 난수 초기값을 설정해주면 됩니다. (아래 코드를 실행하면 저와 동일한 난수 값으로 구성된 텐서를 반환할 것입니다.)
## setting a seed number for reproducibility
torch.manual_seed(1004)
torch.rand(2, 4)
# tensor([[0.9716, 0.3893, 0.2629, 0.9071],
# [0.1041, 0.0360, 0.1655, 0.7124]])
(1-2) torch.randn(size) : 표준정규분포 X~N(0, 1)로 부터 난수를 생성해서 텐서 만들기
평균이 0, 표준편차가 1인 표준정규분포 X~N(0, 1) 로 부터 실수 난수를 생성해서 텐서를 만들어줍니다.
# generating a tensor from a standard normal distribution, X~N(0, 1)
torch.randn(2, 4)
# tensor([[ 1.0868, -1.5346, -0.4525, 0.3689],
# [-0.9079, -0.2578, -0.3581, 0.4072]])
(1-3) torch.randint(low, high, size) : low~high 사이의 정수로 난수를 생성해서 텐서 만들기
이때 low 값은 포함되고, high 값은 포함되지 않습니다.
## generating a tensor with random integers
## (including the low value, but not including the high value)
torch.randint(low=0, high=10, size=(2, 4))
# tensor([[9, 2, 7, 8],
# [5, 3, 0, 8]])
(1-4) torch.randperm(the upper bound, n) : 0~n 사이의 정수를 무작위로 섞어서 텐서 만들기
아래의 예처럼 upper bound 'n' 이 '10' 이면 0~9 까지의 정수 (10은 미포함) 를 모두 사용해서 무작위로 섞어서 텐서를 만들어줍니다.
## returns a random permutation of integers from 0 to n
torch.randperm(10)
# tensor([5, 3, 2, 7, 6, 9, 4, 1, 8, 0])
2. 인풋과 동일한 형태(same shape as input tensor)로 난수를 생성해서 PyTorch tensor 만들기
(2-1) torch.rand_like(input)
: 인풋과 동일한 형태(shape)로 0~1 사이의 실수로 난수를 생성해서 텐서 만들기
예제로 numpy ndarray 로 (2, 3) 형태의 PyTorch tensor 를 만들어보았습니다.
## creating a tensor object with numpy array
import numpy as np
y = np.array([[1., 2., 3.], [4., 5., 6.]])
z = torch.tensor(y)
print(z)
# tensor([[1., 2., 3.],
# [4., 5., 6.]], dtype=torch.float64)
z.shape
# torch.Size([2, 3])
torch.rand() 가 0~1 사이의 실수에서 난수를 생성해서 텐서를 만들었는데요, torch.rand_like(input) 은 인풋과 같은 형태(shape)로 0~1 사이의 실수에서 난수를 생성해서 텐서를 만들어줍니다.
## Returns a tensor with the same size as input
## that is filled with random numbers
## from a uniform distribution on the interval [0,1)
torch.rand_like(z)
# tensor([[0.6764, 0.6955, 0.1822],
# [0.4265, 0.8873, 0.2876]], dtype=torch.float64)
(2-2) torch.randn_like(input)
: 인풋과 동일한 형태로 표준정규분포 X~N(0,1)에서 난수를 생성해서 텐서 만들기
## Returns a tensor with the same size as input
## that is filled with random numbers from
## a normal distribution with mean 0 and variance 1.
torch.randn_like(z)
# tensor([[-1.2964, -0.0624, 1.2123],
# [ 2.2158, 0.2930, -0.2537]], dtype=torch.float64)
(2-3) torch.randint_like(input, low, high)
: 인풋과 동일한 형태로 low~high 사이의 정수로 난수를 생성해서 텐서 만들기
## Returns a tensor with the same shape as Tensor input
## filled with random integers generated uniformly
## between low (inclusive) and high (exclusive)
torch.randint_like(input=z, low=0, high=10)
# tensor([[7., 6., 8.],
# [2., 9., 1.]], dtype=torch.float64)
이번 포스팅이 많은 도움이 되었기를 바랍니다.
행복한 데이터 과학자 되세요! :-)

'Deep Learning (TF, Keras, PyTorch) > PyTorch basics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [PyTorch] 텐서 나누기 (splitting a PyTorch tensor into multiple tensors) (0) | 2023.02.23 |
|---|---|
| [PyTorch] 텐서 합치기 (concat, stack) (0) | 2023.02.21 |
| [PyTorch] 텐서의 인덱싱과 슬라이싱 (indexing & slicing of PyTorch tensor) (0) | 2023.02.19 |
| [PyTorch] NumPy의 array 대비 PyTorch 의 성능 비교 (0) | 2023.02.19 |
| [PyTorch] 텐서 객체 만들기 (PyTorch tensor objects) (0) | 2023.02.05 |