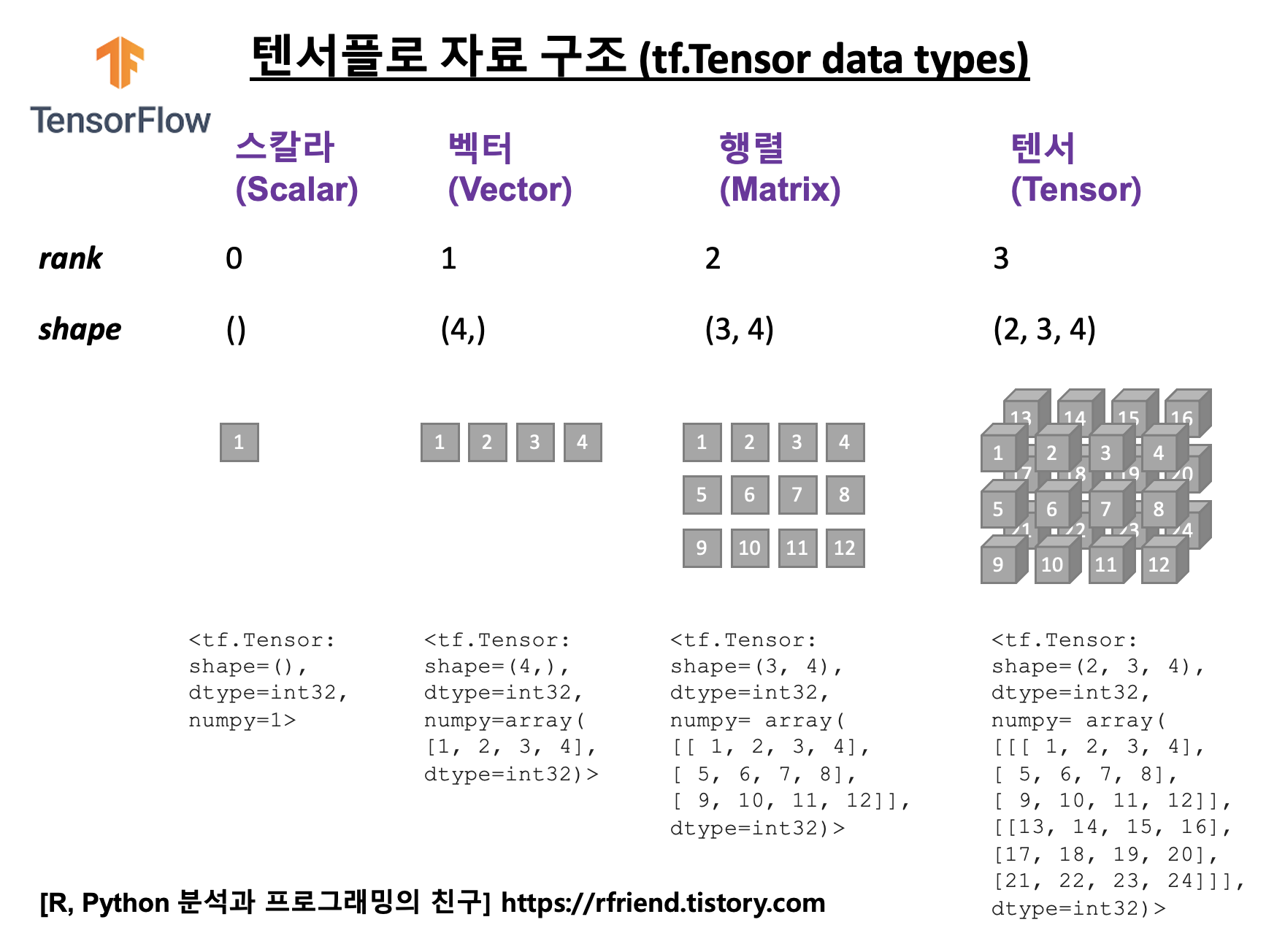
지난번 포스팅에서는 TensorFlow 의 tf.constant() 로 텐서를 만드는 방법(https://rfriend.tistory.com/718)을 소개하였습니다. 이번 포스팅에서는 TensorFlow 의 변수 (Variable) 에 대해서 소개하겠습니다.
(1) TensorFlow 변수(tf.Variable)는 무엇이고, 상수(tf.constant)는 무엇이 다른가?
(2) TensorFlow 변수를 만들고(tf.Variable), 값을 변경하는 방법 (assign)
(3) TensorFlow 변수 연산 (operations)
(4) TensorFlow 변수 속성 정보 (attributes)
(5) 변수를 상수로 변환하기 (converting tf.Variable to tf.constant)
(1) TensorFlow 변수(tf.Variable)는 무엇이고, 상수(tf.constant)와는 무엇이 다른가?
텐서플로의 튜토리얼의 소개를 보면 "변수는 프로그램 연산에서 공유되고 유지되는 상태를 표현하는데 사용을 권장("A TensorFlow variable is the recommended way to represent shared, persistent state your program manipulates.") 한다고 합니다. 말이 좀 어려운데요, 변수와 상수를 비교해보면 금방 이해가 갈 것입니다.
텐서플로 변수(Variable)는 값의 변경이 가능(mutable value)한 반면에, 상수(constant)는 값의 변경이 불가능(immutable value)합니다. 변수는 값의 변경이 가능하고 공유되고 유지되는 특성 때문에 딥러닝 모델을 훈련할 때 자동 미분 값의 back-propagations 에서 가중치를 업데이트한 값을 저장하는데 사용이 됩니다. 변수는 초기화(initialization)가 필요합니다.

(2) TensorFlow 변수를 만들고(tf.Variable), 값을 변경하는 방법 (assign)
TensorFlow 변수는 tf.Variable(value, name, dtype, shape) 의 메소드를 사용해서 만들 수 있습니다.
import tensorflow as tf
print(tf.__version__)
#2.7.0
## After construction, the type and shape of the variable are fixed.
v = tf.Variable([1, 2])
print(v)
#<tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(2,) dtype=int32, numpy=array([1, 2], dtype=int32)>
변수의 값을 변경할 때는 assign() 메소드를 사용합니다. assign_add(), assign_sub() 를 사용해서 덧셈이나 뺄셈 연산을 수행한 후의 결과로 변수의 값을 업데이트 할 수도 있습니다.
## The value can be changed using one of the assign methods.
v.assign([3, 4])
print(v)
#<tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(2,) dtype=int32, numpy=array([3, 4], dtype=int32)>
## The value can be changed using one of the assign methods.
v.assign_add([10, 20])
print(v)
#<tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(2,) dtype=int32, numpy=array([13, 24], dtype=int32)>
tf.Variable(value, shape=tf.TensorShape(None)) 처럼 shape 매개변수를 사용하면 형태(shape)를 정의하지 않은 상태에서 변수를 정의할 수도 있습니다.
## The shape argument to Variable's constructor allows you to
## construct a variable with a less defined shape than its initial-value
v = tf.Variable(1., shape=tf.TensorShape(None))
print(v)
#<tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=<unknown> dtype=float32, numpy=1.0>
v.assign([[1.]])
#<tf.Variable 'UnreadVariable' shape=<unknown> dtype=float32,
#numpy=array([[1.]], dtype=float32)>
(3) TensorFlow 변수 연산 (operations)
변수는 텐서 연산의 인풋(inputs to operations)으로 사용될 수 있습니다. 아래 예에서는 변수와 상수간 원소 간 곱과 합을 구해보았습니다.
## Variable created with Variable() can be used as inputs to operations.
## Additionally, all the operators overloaded for the Tensor class are carried over to variables.
w = tf.Variable([1., 2.])
x = tf.constant([3., 4.])
## element-wise product
tf.math.multiply(w, x)
# <tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=float32, numpy=array([3., 8.], dtype=float32)>
## element-wise addition
w + x
# <tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=float32, numpy=array([4., 6.], dtype=float32)>
(4) TensorFlow 변수 속성 정보 (attributes)
텐서플로의 변수에서 이름(name), 형태(shape), 데이터 유형(dtype), 연산에 이용되는 디바이스(device) 속성정보를 조회할 수 있습니다.
## Attributes
v = tf.Variable([1., 2.], name='MyTensor')
print('name:', v.name)
print('shape:', v.shape)
print('dtype:', v.dtype)
print('device:', v.device)
# name: MyTensor:0
# shape: (2,)
# dtype: <dtype: 'float32'>
# device: /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0
(5) 변수를 상수로 변환하기 (converting tf.Variable to tf.constant)
변수를 상수로 변환하려면 tf.convert_to_tensor(Variable) 메소드를 사용합니다.
## converting tf.Variable to Tensor
c = tf.convert_to_tensor(v)
print(c)
# tf.Tensor([1. 2.], shape=(2,), dtype=float32)
[ Reference ]
* TensorFlow Variable: https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Variable
이번 포스팅이 많은 도움이 되었기를 바랍니다
행복한 데이터 과학자 되세요! :-)

'Deep Learning (TF, Keras, PyTorch)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Tensorflow] 딥러닝을 위한 공개 데이터셋 Tensorflow Datasets (3) | 2020.03.19 |
|---|---|
| [Keras] 이미지 파일 업로드하고 전처리하여 시각화하는 방법 (how to upload, preprocess and visualize images) (52) | 2019.03.05 |
| Tensorflow, Keras가 GPU를 사용하고 있는지 확인하는 방법 (0) | 2019.02.19 |
| [Keras] TypeError: softmax() got an unexpected keyword argument 'axis' 에러 시 tensorflow upgrade (0) | 2019.02.06 |
| 집에서 딥러닝 공부하기에 적합한 PC 사양 및 가격대 (2017-09월) (9) | 2017.09.17 |