[Python] 텍스트를 단어 단위로 파싱해서 One-hot encoding 하기 (parsing text and one-hot encoding at word-level)
Deep Learning (TF, Keras, PyTorch)/Natural Language Processing 2019. 5. 22. 00:32텍스트 분석을 할 때 제일 처음 하는 일이 문서, 텍스트를 분석에 적합한 형태로 전처리 하는 일입니다.
이번 포스팅에서는 (1) 텍스트 데이터를 Python의 string methods 를 이용하여 단어 단위로 파싱(parsing text at word-level) 한 후에, 단어별 index를 만들고, (2) 텍스트를 단어 단위로 one-hot encoding 을 해보겠습니다.
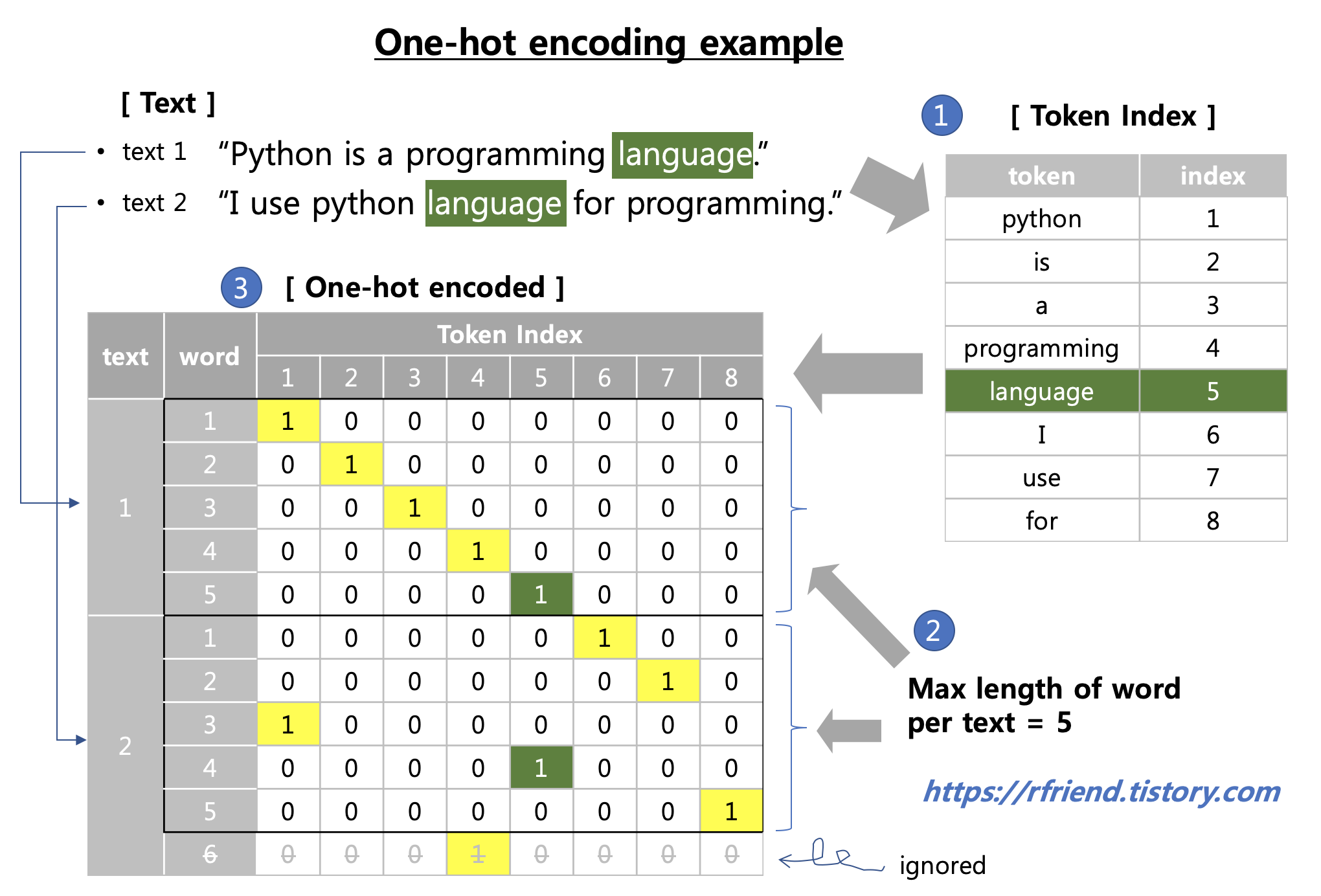
1. 텍스트 데이터를 Python string methods를 사용하여 단어 단위로 파싱하고, 단어별 token index 만들기
예제로 사용할 텍스트는 Wikipedia 에서 검색한 Python 영문 소개자료 입니다.
# import modules
import numpy as np
import os
# set directory
base_dir = '/Users/ihongdon/Documents/Python/dataset'
file_name = 'python_wikipedia.txt'
path = os.path.join(base_dir, file_name)
# open file and print it as an example
file_opened = open(path)
for line in file_opened.readlines():
print(line)|
Python programming language, from wikipedia
|
아래는 Python string method를 사용해서 텍스트에서 단어를 파싱하고 전처리할 수 있는 사용자 정의 함수 예시입니다. 가령, 대문자를 소문자로 바꾸기, stop words 제거하기, 기호 제거하기, 숫자 제거하기 등을 차례대로 적용할 수 있는 기본적인 예시입니다. (이 역시 텍스트 분석용 Python module 에 잘 정의된 함수들 사용하면 되긴 합니다. ^^;)
# UDF of word preprocessing
def word_preprocess(word):
# lower case
word = word.lower()
# remove stop-words
stop_words = ['a', 'an', 'the', 'in', 'with', 'to', 'for', 'from', 'of', 'at', 'on',
'until', 'by', 'and', 'but', 'is', 'are', 'was', 'were', 'it', 'that', 'this',
'my', 'his', 'her', 'our', 'as', 'not'] # make your own list
for stop_word in stop_words:
if word != stop_word:
word = word
else:
word = ''
# remove symbols such as comma, period, etc.
symbols = [',', '.', ':', '-', '+', '/', '*', '&', '%', '[', ']', '(', ')'] # make your own list
for symbol in symbols:
word = word.replace(symbol, '')
# remove numbers
if word.isnumeric():
word = ''
return word
다음으로, python_wikipedia.txt 파일을 열어서(open) 각 줄 단위로 읽고(readlines), 좌우 공백을 제거(strip)한 후에, 단어 단위로 분할(split) 하여, 위에서 정의한 word_preprocess() 사용자 정의 함수를 적용하여 전처리를 한 후, token_idx 사전에 단어를 Key로, Index를 Value로 저장합니다.
# blank dictionary to store
token_idx = {}
# opening the file
file_opened = open(path)
# catching words and storing the index at token_idx dictionary
for line in file_opened.readlines():
# strip leading and trailing edge spaces
line = line.strip()
# split the line into word with a space delimiter
for word in line.split():
word = word_preprocess(word) # UDF defined above
# put word into token_index
if word not in token_idx:
if word != '':
token_idx[word] = len(token_idx) + 1
단어를 Key, Index를 Value로 해서 생성된 token_idx Dictionary는 아래와 같습니다.
token_idx| {'"batteries': 48, '1980s': 56, '2x': 87, 'abc': 58, 'about': 80, 'aims': 28, 'amount': 81, 'approach': 27, 'available': 104, 'backwardcompatible': 74, 'capable': 67, 'clear': 32, 'code': 18, .... 중간 생략 .... 'successor': 57, 'support': 83, 'supports': 40, 'system': 66, 'systems': 107, 'the': 84, 'typed': 38, 'unmodified': 78, 'use': 22, 'van': 10, 'whitespace': 24, 'wikipedia': 4, 'write': 31, 'written': 82} |
token_idx.values()| dict_values([104, 96, 102, 112, 68, 111, 21, 18, 8, 15, 20, 47, 37, 16, 74, 89, 57, 117, 19, 93, 83, 76, 91, 43, 30, 32, 54, 33, 35, 98, 64, 80, 17, 34, 10, 61, 50, 46, 49, 23, 72, 67, 119, 95, 14, 3, 116, 81, 85, 1, 99, 51, 77, 38, 90, 118, 120, 100, 101, 9, 39, 12, 123, 84, 122, 69, 26, 115, 88, 13, 36, 60, 5, 6, 75, 103, 66, 94, 78, 97, 121, 55, 108, 109, 58, 4, 82, 41, 79, 87, 29, 106, 114, 113, 105, 73, 45, 71, 24, 2, 53, 31, 86, 11, 22, 42, 59, 7, 110, 40, 56, 70, 92, 28, 27, 48, 62, 44, 107, 65, 25, 52, 63]) |
총 123개의 단어가 있으며, 이 중에서 'python'이라는 단어는 token_idx에 '1' 번으로 등록이 되어있습니다.
max(token_idx.values())| 123 |
token_idx.get('python')| 1 |
2. 텍스트를 단어 단위로 One-hot encoding 하기
하나의 텍스트 문장에서 고려할 단어의 최대 개수로 max_len = 40 을 설정하였습니다. (한 문장에서 41번째 부터 나오는 단어는 무시함). 그리고 One-hot encoding 한 결과를 저장할 빈 one_hot_encoded 다차원 배열을 np.zeros() 로 만들어두었습니다.
# consider only the first max_length words in texts
max_len = 40
# array to store the one_hot_encoded results
file_opened = open(path)
one_hot_encoded = np.zeros(shape=(len(file_opened.readlines()),
max_len,
max(token_idx.values())+1))
one_hot_encoded 는 (5, 40, 124) 의 다차원 배열입니다. 5개의 텍스트 문장으로 되어 있고, 40개의 최대 단어 길이(max_len) 만을 고려하며, 총 124개의 token index 에 대해서 해당 단어가 있으면 '1', 없으면 '0'으로 one-hot encoding을 하게 된다는 뜻입니다.
one_hot_encoded.shape| (5, 40, 124) |
아래는 파일을 열고 텍스트를 줄 별로 읽어 들인 후에, for loop 을 돌면서 각 줄에서 단어를 분할하고 전처리하여, token_idx.get(word) 를 사용해서 해당 단어(word)의 token index를 가져온 후, 해당 텍스트(i), 단어(j), token index(idx)에 '1'을 입력하여 one_hot_encoded 다차원 배열을 업데이트 합니다.
file_opened = open(path)
for i, line in enumerate(file_opened.readlines()):
# strip leading and trailing edge spaces
line = line.strip()
for j, word in list(enumerate(line.split()))[:max_len]:
# preprocess the word
word = word_preprocess(word)
# put word into token_index
if word != '':
idx = token_idx.get(word)
one_hot_encoded[i, j, idx] = 1.
이렇게 생성한 one_hot_encoded 다차원배열의 결과는 아래와 같습니다.
one_hot_encoded| array([[[0., 1., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 1., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], ..., [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.]], [[0., 1., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], ..., [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.]], [[0., 1., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], ..., [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.]], [[0., 1., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], ..., [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.]], [[0., 1., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], ..., [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 1.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.]]]) |
type(one_hot_encoded)| numpy.ndarray |
이해를 돕기 위하여 python_wikipedia.txt 파일의 첫번째 줄의, 앞에서 부터 40개 단어까지의 단어 중에서, token_idx 의 1번~10번 까지만 one-hot encoding이 어떻게 되었나를 단어와 token_idx 까지 설명을 추가하여 프린트해보았습니다. (말로 설명하려니 어렵네요. ㅜ_ㅜ)
# sort token_idx dictionary by value
import operator
sorted_token_idx = sorted(token_idx.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1))
# print out 10 words & token_idx of 1st text's 40 words as an example
for i in range(10):
print('word & token_idx:', sorted_token_idx[i])
print(one_hot_encoded[0, :, i+1])| word & token_idx: ('python', 1) [1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] word & token_idx: ('programming', 2) [0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] word & token_idx: ('language', 3) [0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] word & token_idx: ('wikipedia', 4) [0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] word & token_idx: ('interpreted', 5) [0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] word & token_idx: ('highlevel', 6) [0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] word & token_idx: ('generalpurpose', 7) [0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] word & token_idx: ('created', 8) [0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] word & token_idx: ('guido', 9) [0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] word & token_idx: ('van', 10) [0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] |
많은 도움이 되었기를 바랍니다.

'Deep Learning (TF, Keras, PyTorch) > Natural Language Processing' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [NLP] TF-IDF (Term Frequency - Inverse Document Frequency) (2) | 2022.04.10 |
|---|---|
| [NLP] 언어 구조의 구성 요소 (Building Blocks of Language Structure) (0) | 2022.02.20 |
| [NLP] 자연어 처리(NLP, Natural Language Processing)란 무엇이고, NLP 응용분야는 무엇이 있나? (0) | 2022.02.20 |
| [Python] 텍스트로부터 CSR 행렬을 이용하여 Term-Document 행렬 만들기 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Python] NLTK(Natural Language Toolkit)와 WordNet으로 자연어 처리하기 맛보기 (0) | 2020.08.02 |